1. Introduction
Breast cancer remains a leading health concern for women around the world, with early detection playing a critical role in improving survival rates. Traditional diagnostic tools such as mammography, while widely used, come with notable limitations—radiation exposure, discomfort, and reduced effectiveness in dense breast tissue, especially in younger women. This is where the innovative concept described in US20120065539A1 offers a significant breakthrough.
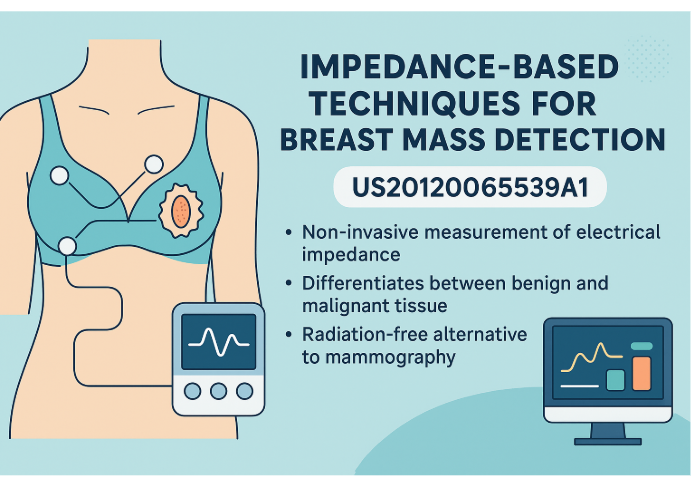
This patent proposes a method that utilizes electrical impedance to detect breast abnormalities. Unlike mammograms, this approach is non-invasive and free of ionizing radiation, making it safer and more suitable for frequent use.
The technology outlined in US20120065539A1 represents a new frontier in diagnostic healthcare by enabling early, accurate, and comfortable breast mass detection.
2. Technical Background
Principles of Bio-Impedance
Electrical impedance refers to how much a material resists the flow of an electric current. In biological tissues, different types of cells and structures respond differently to electrical signals. This concept is the basis for bio-impedance, a technique that has been used in other areas of medicine for assessing body composition and hydration.
In the context of US20120065539A1, bio-impedance is applied to breast tissue to detect the presence of masses. Abnormal tissues, such as tumors, have distinct electrical properties compared to normal tissue. By sending small electrical currents through the breast and measuring the response, clinicians can detect potential issues that warrant further investigation.
Challenges with Current Diagnostic Tools
While traditional imaging technologies are effective, they also pose several challenges:
| Diagnostic Method | Limitation |
|---|---|
| Mammography | Radiation exposure, discomfort, limited use in dense tissue |
| Ultrasound | Operator-dependent, not always definitive |
| MRI | Expensive, not accessible for all patients |
US20120065539A1 aims to overcome these limitations by offering a safer, more accessible alternative.
3. Summary of the Invention
The core idea behind US20120065539A1 is to develop a medical device that can non-invasively detect breast abnormalities by measuring the electrical impedance of tissue. This device sends low-frequency electrical signals through the breast and interprets the returning signal to identify anomalies.
Key Benefits of the Invention
- No radiation – Safe for repeated use, even in younger women.
- Non-invasive – Does not require tissue penetration or compression.
- Quick results – Immediate feedback using visual or audio indicators.
- Portable – Can be used in clinics or even integrated into wearable items like bras.
4. Detailed Description of the Invention
Device Configuration
The system described in US20120065539A1 includes several key components:
- A signal generator to create electrical impulses.
- Source and receiving electrodes placed on or near the breast.
- A processor that analyzes the signal response.
- A display or alert system to communicate findings.
A unique aspect of the invention is how it proposes embedding electrodes in everyday wearables, such as a brassiere, allowing for continuous or routine monitoring without discomfort.
How It Works
The operation is relatively simple yet highly effective:
- The device generates electrical signals across a range of frequencies.
- These signals are applied to the breast tissue via surface electrodes.
- The response of the tissue—measured as impedance—is recorded.
- The data is processed to identify abnormal patterns that suggest a mass.
- Results are displayed visually (e.g., with a color-coded system) or through sound or vibration alerts.
Data Processing and Analysis
The system uses a proprietary algorithm that compares collected impedance values to known patterns of healthy and abnormal tissues. Based on this analysis, it can differentiate between benign and malignant growths with impressive accuracy.
User Feedback Features
To ensure user-friendliness, the device provides instant feedback through:
- LED indicators showing green (normal), yellow (suspicious), and red (abnormal) statuses.
- Vibratory or sound alerts to notify users discreetly.
- Graphical displays on a screen for professional evaluation.
5. Applications and Use Cases
US20120065539A1 is not limited to clinical settings. Its design allows for broader use across different environments and patient needs.
Primary Use Cases
- Routine screening: Especially beneficial for individuals at high risk or those with dense breast tissue.
- Ongoing monitoring: For patients under observation post-treatment.
- Comparative analysis: To detect asymmetry between both breasts.
Potential for Other Medical Applications
While the focus is breast mass detection, the technique has broader potential, such as:
| Tissue Type | Application |
|---|---|
| Lung | Tumor detection or monitoring pulmonary disease |
| Prostate | Identifying prostate enlargement or cancer |
| Muscle & Skin | Detecting localized infections or growths |
6. Advantages and Innovations
The technology outlined in US20120065539A1 offers a significant step forward in early cancer detection and patient comfort. Among its key advantages:
- Improved diagnostic accuracy: Electrical impedance is sensitive to subtle tissue changes.
- Patient comfort: No squeezing, needles, or radiation involved.
- Ease of use: Could be self-administered or used in non-specialist settings.
- Cost-effective: Reduces the need for expensive imaging unless absolutely necessary.
7. Patent Claims
The patent includes detailed claims that describe both the physical components and the processes involved. These claims protect the invention’s unique approach to:
- Measuring impedance across multiple frequencies.
- Analyzing tissue using signal comparison algorithms.
- Displaying diagnostic feedback through user-friendly interfaces.
- Integrating sensors into wearable designs for real-time data collection.
8. Figures and Illustrations
To support the detailed description, US20120065539A1 includes diagrams and charts that show:
- Electrode placement on the body.
- Flow of electrical signals.
- Example outputs that differentiate between tissue types.
These illustrations are essential for understanding how the device functions in real-world applications.
9. Conclusion
The patent US20120065539A1 introduces a compelling alternative to traditional breast cancer detection methods. By leveraging electrical impedance, it provides a safer, more accessible, and more comfortable diagnostic tool that can be used frequently without side effects.
Its non-invasive nature, ease of use, and cost-efficiency position it as a transformative innovation in women’s healthcare. With further development, this technology could extend to detecting various other tissue abnormalities, marking a new era in diagnostic medicine.
Related Articles
Discover Life at Kimaree 7080 Highway 61 Apt 102: Comfort, Community & Convenience in Barnhart, MO
Discover MobileCreativeorg: Your Complete Guide to Mobile Innovation, Design & Development
Discover TributeonPrintedPics: Turn Cherished Memories Into Beautiful Keepsakes
Gel Ooru: Exploring Its Cultural Heritage, Wellness Benefits, and Modern Uses